Introduction to Coffee Cultivation
Coffee, a beloved beverage enjoyed by millions worldwide, has a rich history that traces back to its origins in the region of Ethiopia during the 15th century. From then on, its journey has expanded across the globe, solidifying its place as one of the most consumed drinks, second only to water. The fascination with coffee lies not only in its energizing properties but also in its unique flavor profiles and the cultural significance it holds in various societies. Understanding how coffee grows is essential, as it highlights the intricate processes and dedication required to produce this global staple.
At the heart of coffee cultivation is the coffee tree, known for producing the coffee cherries from which the beans are extracted. These trees thrive in specific climates, typically found in the “coffee belt,” a region around the equator encompassing parts of Africa, Asia, and Central and South America. Conditions such as altitude, temperature, and rainfall significantly influence the quality and characteristics of the beans. Coffee beans grow on trees that can reach heights of up to 30 feet, though most growers keep them shorter for easier harvesting. It takes about three to five years for a coffee seed to mature into a fully productive coffee tree, and understanding this timeline is crucial for both aspiring growers and enthusiasts alike.
The process of growing coffee involves meticulous planning and management, as various factors can impact yield and quality. Practices such as shade management, pruning, and fertilization are integral to ensuring healthy trees. Moreover, farmers often engage in both traditional and modern agricultural techniques to enhance productivity while preserving the environment. The relationship between coffee, the grower, and the land underscores the importance of ethical sourcing and sustainable practices in the coffee industry, leading to a more profound appreciation for the journey from seed to sip.
The Coffee Plant: Varieties and Characteristics
The coffee plant, primarily categorized into two main varieties, Arabica and Robusta, plays a crucial role in the global coffee industry. Arabica coffee, scientifically known as Coffea arabica, is renowned for its smooth flavor and nuanced aroma, often exhibiting characteristics ranging from mild and sweet to fruity and floral. This variety typically flourishes at higher elevations, requiring a cooler climate with consistent rainfall. On the other hand, Robusta, or Coffea canephora, is more resilient and robust, thriving in lower altitudes and warmer environments. While Robusta coffee beans on trees yield a stronger and somewhat bitter flavor profile, they are also more resistant to pests and diseases.
Understanding the growing conditions of these coffee varieties is vital. Arabica plants thrive in a temperature range between 60°F to 70°F, preferring rich, well-draining soil that allows for healthy root development. Conversely, Robusta can tolerate higher temperatures, making it a popular choice in various regions, particularly in Africa and Southeast Asia, where the climate supports its growth. Given the different growth requirements, can I grow coffee beans successfully? It often depends on the chosen variety and the climatic conditions available.
The distinction between Arabica and Robusta goes beyond growing conditions; it also significantly affects flavor and quality. Arabica coffee accounts for approximately 60-70% of global coffee production, largely due to its superior taste and complexity. In contrast, while Robusta may yield higher quantities, its flavors tend to be earthier and stronger, appealing to different consumer preferences. Thus, for those contemplating the question, “how does coffee grow?” understanding the characteristics of these two varieties is essential. Each has its own unique set of traits that can impact both cultivation and the end beverage experience, making them indispensable to coffee growers and enthusiasts alike.
The Lifecycle of a Coffee Plant
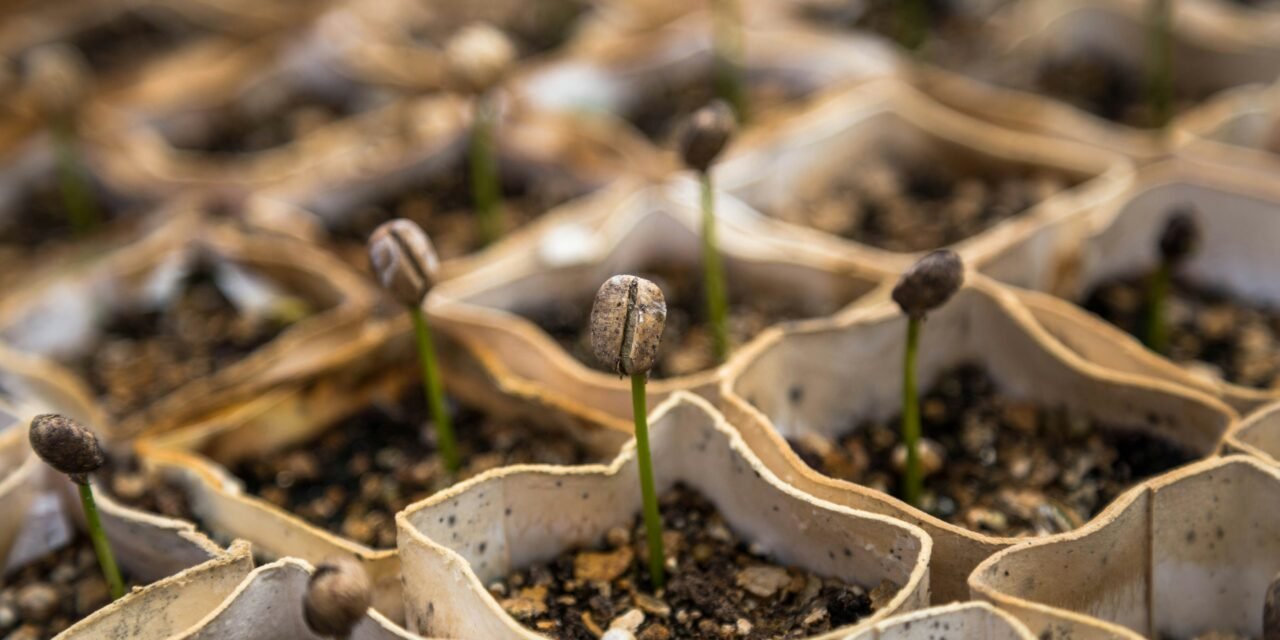
The lifecycle of a coffee plant is a complex journey that begins with the coffee seed. For aspiring growers wondering, “can I grow coffee beans?”, understanding each stage of this process is essential. The lifecycle typically starts with planting the coffee seeds, which requires a warm, humid environment. The ideal temperature for coffee seed germination ranges from 70 to 85 degrees Fahrenheit. Under optimal conditions, seeds will germinate within 2 to 4 months.
Once germination occurs, seedlings emerge and enter the growth phase. During this stage, young coffee trees require consistent watering, proper fertilizer, and adequate sunlight to develop strong roots and foliage. This period can last between 3 to 4 years as the plants mature and become more resilient. Furthermore, the coffee beans on tree can only develop if the tree grows in the right environmental conditions, such as elevation and soil quality.
After a few years of growth, a coffee tree will begin to flower. The flowering stage is often characterized by white blossoms that emit a sweet fragrance. These flowers typically bloom during the wet season, and the pollination process, mainly executed by bees, usually occurs within a few days. Following successful pollination, the coffee plant will enter the fruiting stage, where it develops cherries. These cherries contain the coffee beans and can take around 6 to 8 months to ripen, depending on the specific coffee variety and climate.
The final phase is harvesting, which often occurs once the cherries have ripened and turned deep red. This process can commence 5 to 7 years after planting. The timing of the harvest plays a crucial role in determining the flavors of the coffee produced. With appropriate care and conditions, growers can successfully navigate each stage and yield high-quality coffee beans.
Ideal Growing Conditions for Coffee
The cultivation of coffee beans is primarily influenced by several environmental factors, including climate, soil, altitude, and rainfall. Coffee plants, specifically the Coffea arabica and Coffea canephora species, thrive in specific conditions that significantly contribute to the quality and flavor of the coffee beans.
Climate plays a crucial role in coffee cultivation. These plants prefer a tropic or subtropical climate where temperatures range between 60°F to 70°F (15°C to 24°C). Extreme cold or frost can damage the delicate coffee plant, impeding the production of coffee seed. Additionally, coffee requires abundant sunlight for optimal growth, but consistent shade is necessary during the hottest parts of the day to prevent sunburn on the leaves. Moreover, coffee does well in regions with at least 40 inches of annual rainfall, distributed evenly throughout the year, although some fluctuations can occur depending on the geographical area.
Soil quality is equally important for coffee beans to grow successfully. Coffee plants flourish in well-drained, fertile soils enriched with organic matter. Soils derived from volcanic ash, which are typically found in many coffee-growing regions, offer excellent drainage and high nutrient availability, fostering healthy growth. The ideal pH level for coffee soil is between 6 and 6.5, ensuring that the plants can absorb essential nutrients efficiently.
Altitude also influences the maturation of coffee beans on tree. Arabica coffee, known for its sweet and nuanced flavors, is often grown at higher altitudes ranging from 2,000 to 6,000 feet. In contrast, Robusta coffee can thrive at lower elevations. The cooling effect of higher altitudes slows down the growth rate of coffee beans, which allows for more complex flavor development. Central and South America, along with regions in Africa and Asia, offer optimal conditions for these coffee varieties, making them prominent areas for coffee production.
Coffee Farming Practices: Sustainable vs. Conventional
Coffee farming practices vary significantly, with two primary methods being sustainable and conventional approaches. Sustainable coffee farming emphasizes environmental responsibility and aims to minimize ecological damage. Practices within this method include shade-grown coffee cultivation, which allows coffee plants to thrive under the canopy of trees, thereby encouraging biodiversity and promoting soil health. Organic farming also falls under sustainable practices, using natural fertilizers and pest control methods, avoiding synthetic chemicals that could harm the environment.
The flavor and quality of coffee beans can be influenced by these sustainable practices. For instance, coffee beans grown under shade often develop a richer, more complex flavor profile. The biodiversity supported by shade-grown environments can yield unique flavor notes not found in conventionally grown beans. Conversely, conventional coffee farming often prioritizes higher yields through methods such as monoculture and the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides. While these practices may produce coffee beans more quickly and on a larger scale, they can negatively impact the flavor profile and quality of the coffee. Conventional approaches often lead to poorer soil quality and may contribute to environmental degradation.
In terms of economic impact, sustainable farming practices can improve the livelihoods of farmers over time. By producing high-quality, eco-friendly coffee, farmers can access specialty markets, garnering higher prices for their coffee beans. This could create a more stable income for farmers, who often struggle with the volatility of coffee prices in conventional markets. Sustainable practices not only focus on producing quality coffee seeds but also address the long-term viability of farming communities. Ultimately, the choice between sustainable and conventional methodologies significantly influences how coffee beans grow on trees, the flavor of the final product, and the well-being of those farming them.
The Harvesting Process
The harvesting of coffee cherries is a critical step in the journey from coffee seed to the final brew. It involves a careful selection process, as the timing of the harvest significantly impacts the quality of the resultant coffee beans. Coffee trees typically yield their first cherries about three to five years after planting. The optimal time for harvesting is essential since cherries do not all ripen at once. This means that various methods may be necessary to collect the cherries effectively.
There are two primary methods employed for harvesting coffee cherries: manual and mechanical. Manual harvesting remains the most traditional approach and is widely utilized in regions where high-quality coffee is a priority. This method involves skilled laborers who selectively handpick only the ripest cherries, ensuring that the coffee beans on the tree are collected at peak maturity. The advantage of this technique lies in its ability to produce higher-quality coffee, as only the best cherries are picked, minimizing the inclusion of under-ripe or overripe fruit.
In contrast, mechanical harvesting has gained popularity, particularly in larger coffee plantations where labor costs can be a significant factor. This approach uses specialized machines that can shake the coffee trees, causing ripe cherries to fall. While this method allows for faster harvesting and can be more cost-effective, it often results in a mixture of ripe and unripe cherries being collected. Consequently, this may lead to variations in the quality of the coffee produced, as the presence of lesser-quality cherries can affect the flavor profile of the beans.
Ultimately, the choice between manual and mechanical harvesting depends on the specific goals of the coffee producer, including considerations regarding the quality of the final product. While both methods are effective in their own right, the careful selection associated with manual harvesting often results in superior coffee, emphasizing the importance of understanding how coffee beans grow and the nuances involved in their collection.
Processing Coffee: From Cherry to Bean
The transformation of coffee from cherry to bean is a meticulous process that significantly influences the flavor profile of the final product. After coffee beans reach the optimal ripeness on the tree, they are harvested, typically by hand, ensuring only the best cherries are selected. Once harvested, the cherries undergo processing to separate the coffee seeds, commonly known as coffee beans, from their fruit.
There are two primary methods of processing coffee: the wet method and the dry method. The wet method, also known as the washed method, involves removing the cherry’s outer pulp through fermentation, allowing for a cleaner taste in the coffee. The cherries are soaked in water, which triggers the fermentation process. Once the pulp is removed, the beans are washed to eliminate any remaining mucilage, followed by drying under the sun or using mechanical dryers. This method is known to enhance the acidity and brightness of the coffee flavor.
Conversely, the dry processing method, also referred to as natural processing, entails drying the cherries in the sun before removing the outer layers. This approach allows the beans to absorb sugars from the fruit, often resulting in a fuller body and rich, fruity notes. While easier and less labor-intensive, this method requires careful monitoring to prevent spoilage due to moisture.
After the initial processing stage, the next step is milling, where the dried coffee beans are hulled to remove any remaining parchment or husk. This stage is crucial, as improper milling can lead to defects that adversely affect the coffee’s flavor. Ultimately, the processing techniques employed have a profound effect on how coffee grows in terms of taste and quality and play a vital role in the overall journey of coffee from seed to sip.
Can You Grow Coffee at Home?
Growing coffee at home is indeed a feasible endeavor for those interested in cultivating their own coffee plants. To begin this journey, it is essential to understand that coffee beans grow on trees, specifically from the Coffea genus. This presents a unique challenge, as these trees are native to tropical and subtropical climates. Therefore, individuals residing in cooler regions may need to create a controlled environment, such as a greenhouse, to replicate the warmth and humidity coffee trees require. If you’re asking yourself, “can I grow coffee beans?” the answer is yes, with the right conditions.
When considering how to grow coffee, it’s important to procure quality coffee seeds, as the process starts with planting these coffee seeds. Opt for Arabica or Robusta varieties, which are among the most commonly cultivated. The potting soil should be well-draining, rich in organic matter, and maintain a slightly acidic pH level. Ensure that your planting pot has sufficient drainage holes to prevent overwatering, which could damage the coffee seed.
Light is another critical factor. Coffee trees thrive in dappled sunlight, so partial shade to bright indirect light is ideal. Placing your coffee plant near a south-facing window can help achieve optimal light exposure. Care for your coffee plants includes regular watering and fertilization during the growing season, ensuring that the soil remains moist but not soggy. To answer the question, “how long does it take to grow coffee beans?” patience is required, as it typically takes around three to four years for the trees to mature and produce cherries, from which the coffee beans are harvested. With proper nurturing and the right care instructions, growing coffee beans at home can be a rewarding experience.
Conclusion: The Global Impact of Coffee Cultivation
The journey of coffee, from seed to sip, encompasses a multitude of processes that are both intricate and compelling. Understanding how coffee beans grow on trees provides insight into the effort and time invested in every cup of coffee consumed globally. Initially, coffee seeds are planted in nutrient-rich soil, where they undergo germination, typically taking several months. Once sprouted, the coffee saplings require careful nurturing and ideal climatic conditions to thrive, taking approximately three to four years to grow coffee beans on tree branches that bear ripe cherries ready for harvest.
Interestingly, the cultivation of coffee yields not just a beverage but also significantly affects the cultural, economic, and social landscapes of various regions. In many countries, it is a staple agricultural product that shapes livelihoods. Communities dependent on coffee farming often experience a boost in their economy due to both domestic and export sales. Additionally, the coffee industry creates numerous job opportunities, from cultivation to processing, thereby contributing to socio-economic stability in rural areas.
Culturally, coffee has transcended its role as merely a morning stimulant; it serves as a social lubricant, uniting individuals in various settings, from casual gatherings to formal meetings. It is often celebrated in rituals and traditions across different societies, symbolizing hospitality and connection.
Moreover, as global awareness of sustainable farming practices grows, more farmers are exploring organic methods to cultivate coffee. This approach not only enhances the quality of the coffee seed but also promotes environmental sustainability. As consumers, appreciating the intricate journey of coffee can enrich our experience, allowing us to savor the depth and complexity of flavors derived from such a significant global crop. Ultimately, understanding how coffee beans are grown prompts us to value our next cup much more deeply.